The need for a SEO checklist is vital for every SEO and business owner that seeks organic traffic from Google.
With every major update, Google adds, deletes or replaces major ranking factors. For SEOs like us, it becomes almost impossible to keep a track of all of these factors while working on a website.
Hence, I have compiled this ever-growing list of SEO factors that impact Google rankings.
The checklist is divided into On Page SEO, Off Page SEO and Technical SEO.
On Page SEO Checklist
On Page SEO basically refers to every optimization that can be done on the website to help it rank better. These are adjustments in text, multimedia, links, etc., and are the most important part of doing SEO.
In my experience as an SEO since 2018, I have observed on-page SEO to contribute 60% to 70% in ranking a page on Google. This is the first thing that I do as an SEO for any client website.
1. Keywords
These are the words using which someone searches for anything on Google. For example if someone is searching for best horror movies to watch, the keyword would be “best horror movies” or “imdb horror movies list“.
Keywords can be either short tailed version or long tail versions.
If we take the above example of keyword “best horror movies“, then:
- best horror movies is the core keyword or the short tail version.
- best horror movies in 2024 is the long tail version. Some other long tail versions of the same keyword are:
- best horror movies to watch with kids
- best horror movies from Japan
- best horror movies by James Wan
- best horror movies starring Patrick Wilson
Note that the core keyword is still the same, but the nature of the search differs in the longtail versions.
Generally it is easier to rank for the long tailed versions for most websites and this is how we at Ingeniare SEO target keywords for new websites too.
2. Search Intent
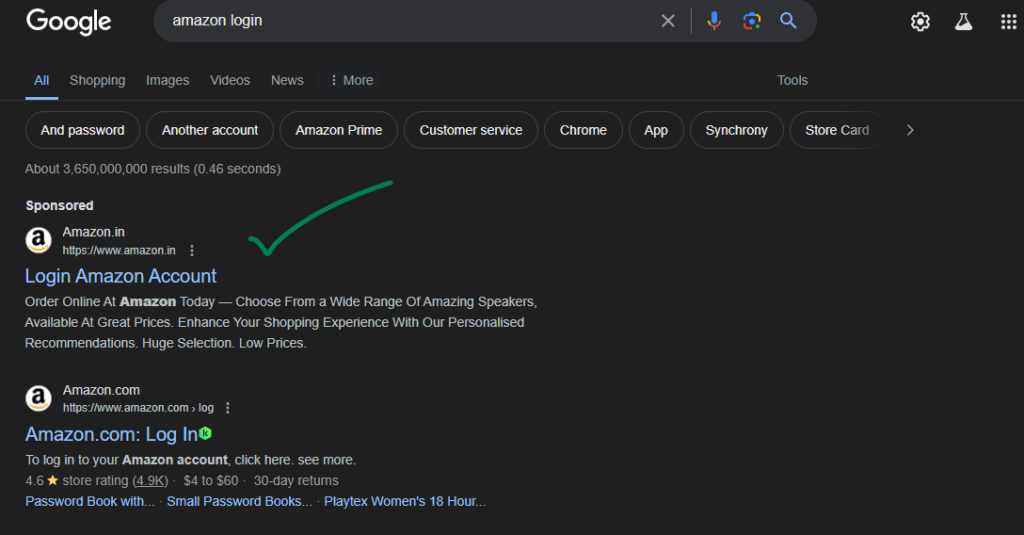
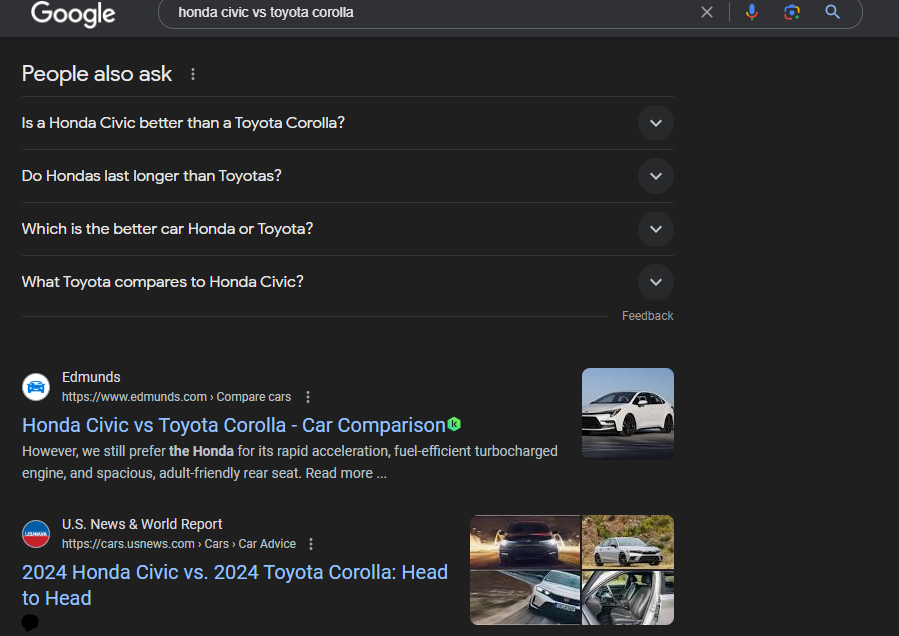
This is the reason why a person is searching something on Google. It can be information such as “top horror movies in 2014” or navigational such as “amazon login”. There are two other common categories as well such as commercial (ex. “Honda Civic vs Toyota Corolla”) and transactional (ex. “premium sports shoes”).
- Informational keywords provide information that a user might need. For example, this article provides information on all the SEO factors that you might need to rank better on Google.
- Navigational keywords are those which a person searches to get to a website or a certain web page. This is because either the URL is long or because it is hard to remember. A simple Google search like “Amazon Login” gets you to the login page in seconds.
- Commercial keywords are those which have a purchase intent associated with it but the searcher is still not sure what specifically do they want to buy. For example, a comparison between “Honda Civic and Toyota Corolla” could be a classic example.
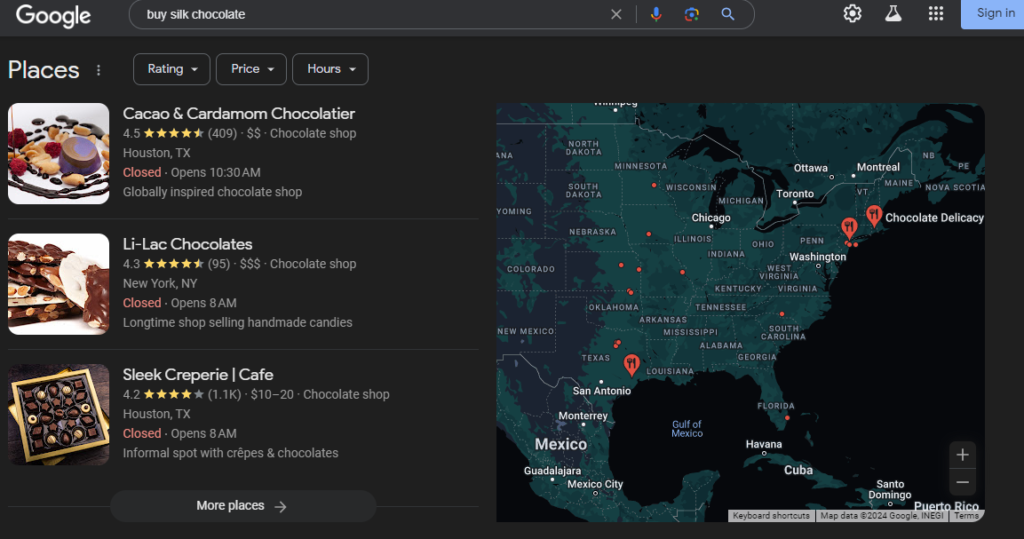
- Transactional Keywords are those which are done solely for the purpose of a transaction. For example, “buy silk chocolate” is a transactional keyword where the intent as well as product is already fixed in the mind of the buyer.
3. Title and Meta Descriptions
These are the first pieces of information from your website that is visible on Google. There is a limit for the length of title and meta description, otherwise they will get truncated on search results page. Though there is no fixed character length, yet we use the indicative figures below to keep our text under check.
- The title should be within 55 characters.
- The description should be less than 160 characters.
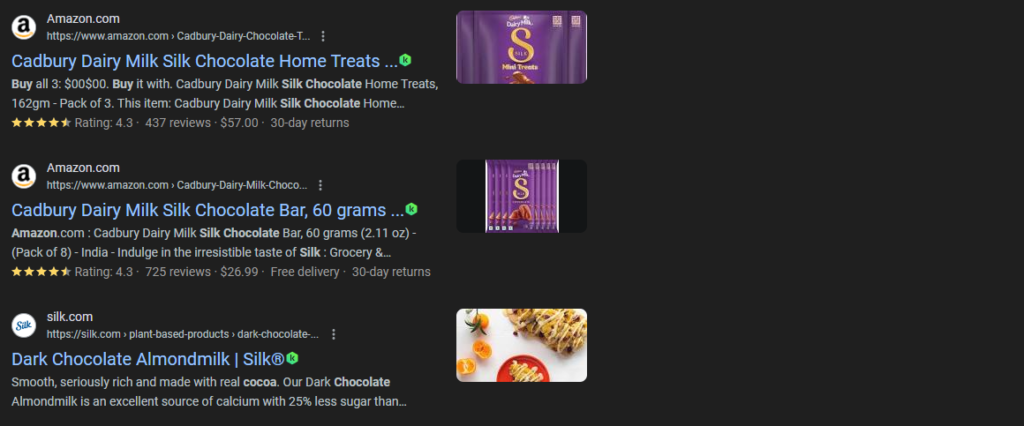
The image above shows three search results.
- In the first and second search result, both the meta title and meta descriptions have exceeded the above limits and are therefore truncated.
- But, in the third result, the meta title fits the limit and is completely shown. However, the meta description is truncated.
Also, it has been commonly observed by most SEOs including me that the meta description usually differs than what was originally provided by the website owner or writer.
After the introduction of Google SGE, the meta description is usually generated by Google based on your website content. Yet, I recommend inserting the meta description manually to make sure no stone is left unturned for your website.
4. Headers – H1, H2, H3, H4, H5 and H6
Headers are the phrases by which Google judges the importance of a topic/subtopic/piece of text on your website.
Usually it is recommended that:
- H1 should be the page title.
- H2 should be used for subtopics.
- H3, H4 and H5 should be used for further subdivisions within the article.
For example for this article on SEO checklist:
- H1 is Complete Google SEO Checklist: On Page, Off Page and Technical SEO
- H2s are On Page SEO, Off Page SEO and Technical SEO
- H3’s example is this subsection on Headers, i.e., 4. Headers – H1, H2, H3, H4, H5 and H6.
Similarly H4, H5 and H6s can be used. WordPress and most text editors such as Google Docs provide till H6. However, there might be lower or more number of hierarchies based on your choice of editors.
A very common mistake users do is they do not understand that Hierarchies of headers must be maintained in a web page. For example, a user cannot use H1 for Title and H3 for the rest. Or they cannot use H1, H2 and H4 by simply skipping the H3.
These mistakes are not only done by novices but also done by experts. For example, whenever, people copy and paste text from ChatGPT or any other similar AI tool, they fail to check whether the formatting has been properly done. In the case of ChatGPT, the subtopics are usually formatted as H3 instead of H2.
5. Content
Content is the most important part of SEO and hence rightfully called as “Content in the King”. We already have a comprehensive guideline on content creation for SEO. You can check this article and understand the importance of content. However, I have also summarized a few rules below.
How Should Content be as per Google’s Helpful Content Update?
- Content should be comprehensive and must answer user query.
- User must be satisfied with the content and must not need to visit another similar page.
- The content must be written from a point of view to help the user.
- The writer and the website must have sufficient credibility.
What is Spam as per Google Spam Updates?
- Use of repurposed expired domains is considered as spam. Expired domains such as government, educational, medical and/or other domains.
- If you are re-using an old domain, make sure to use it for a similar purpose as earlier.
- For example, an educational website must be used for education and not for casino websites.
- Spun or unedited AI text is also considered as spam.
- Plagiarism is also considered spam when no or very little amount of new information is provided.
- Websites that use cloaked affiliate links are also treated as spam.
- Multiple websites with similar type of URL to maximize SERP domination is also considered spam.
- Multiple websites or pages that funnel users to a specific page are also considered spam.
- Presence of hidden texts and links are also considered spam.
- Keyword stuffing is also considered as spam.
- Trying to manipulate Local SEO by adding blocks of text that list cities and regions which the web page is trying to rank for is also spam.
- Unnatural repetition of similar words or texts is also spam.
- Websites that buy or sell links or do excessive link exchanges are considered spammy.
- List of low quality directory or bookmark sites on your website is also considered spam.
- Misleading websites are also considered spammy.
- Websites that scale content via AI or scraped content from other websites just to rank on Google are also considered spam.
There are several other guidelines, we will soon bring a full guide on how to avoid spam for SEOs.
6. Images and Alt Text
Google also has an image search engine which is used to search about visual things such as charts, images, photographs, depictions, etc.
Alt text plays a critical role in this kind of search. Alt text is the series of words or phrases that lets a search engine know what the image is about. This has been used by Google because prior to the advent of image-based search (which uses computer vision) there was no way to search for an image.
Alt texts act as descriptions for images.
To generate a proper alt text, make sure to describe what the image represents and also include the keyword associated with the image. The keyword must be a short tail or a long tail version of the core keyword for that article/blog post.
You may refer to the section on keywords above if you need a refresher.
7. Videos
Lately, Google has been prioritizing pages with a video content. This is because videos are easier to understand and quickly helps in getting familiar with the topic. This is why you will also find a dedicated video page on your search console dashboard.
If you are using videos on your web page, you should follow the same guidelines as image Alt optimization, i.e, the video title and alt text also should contain two things:
- a description of the video
- a keyword related to the article and video, can be either long-tail or short-tail
Please note that adding a YouTube or Twitter video embed in your page adds little to no benefit in terms of SEO but it surely benefits your user experience.
If a user has low hosting capacity for their website, we suggest to upload the video first on YouTube or Twitter and then add the embed on the page. Alternatively, you can also add a video to a storage service such as Amazon S3 and add the video as a link.
On WordPress, the second way of embedding has the highest benefit in terms of SEO.
8. Internal Links
Internal links are vital in properly distributing link authority within your website. When an external website links to your site, your site obtains some link authority from the website which ultimately builds your domain authority.
Remember while adding internal links in your website, make sure you always keep the link as do follow. This is because the term do follow actually asks Google crawlers to follow the linked webpage and index it.
For those who are worried about delayed indexing, you can use this simple, Google-recommended method.
Always put a link of your new pages in the old pages that are already indexed.
9. External Links
These are the links that originate from your website to an external website. Usually, you should embed external links on your site when you are quoting a fact, referencing a data, quoting an original research or using an image or video from an external site.
Attribution helps the original website its due credit and helps you avoid being flagged as a spammy website.
When embedding external links on your site in any format, be it with anchor text, direct URL or as embedded content, make sure to list everything as no-follow. This will prevent accidental linking to spammy websites.
10. Schema Markup
Schema Markup refers to the code that helps Google differentiate between different types of articles. There are about 800 types of schema markups but you will not need most of them. Some common types are:
- FAQ
- ecommerce
- product
- review
- article
- course
- organization
- local business
A schema markup can be done using one of the following three ways.
JSON
This type of markup uses JSON code to tell Google details such as Article Name, Type, URL, Writer, Date, etc.
Below is a sample Schema Markup JSON Code from semrush.com
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”: “http://schema.org”,
“@type”: “Article”,
“headline”: “My First Article”,
“author”: {
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “John Doe”
},
“datePublished”: “2023-11-11”,
“image”: “image.jpg”
}
</script>
RDF- Resource Descriptive Framework in Attributes
RDFa uses HTML code to convey the article schema.
Below is an example from semrush.com.
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Article</title>
</head>
<body>
<div vocab=”http://schema.org/” typeof=”Article”>
<h1 property=”headline”>My First Article</h1>
<img property=”image” src=”image.jpg” alt=”featured image”>
<p>Written by: <span property=”author” typeof=”Person”>John Doe</span></p>
<p>Published on: <time property=”datePublished” datetime=”2023-11-11″>November 11, 2023</time></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Microdata
Microdata also uses HTML code to show attributes of the article to Google. In the below code from semrush.com, “<div>” marks the schema.
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Article</title>
</head>
<body>
<div itemscope itemtype=”http://schema.org/Article”>
<h1 itemprop=”headline”>My First Article</h1>
<img itemprop=”image” src=”image.jpg” alt=”featured image”>
<p>Written by: <span itemprop=”author”>John Doe</span></p>
<p>Published on: <time itemprop=”datePublished” datetime=”2023-11-11″>November 11, 2023</time></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
11. EEAT Rules
There is a comprehensive article on EEAT. However, we are summarizing it for your convenience:
- Expertise stands for domain expertise of the author
- Experience means the time the author has spent using the product or service which they are writing about.
- Authority stands for the topical authority of the website. Topical authority stems from writing in depth articles on almost all the topics around a core keyword.
- Trust comes from getting backlinks from high quality websites.